All About Table Design,A well-proportioned table balances ergonomics with style.
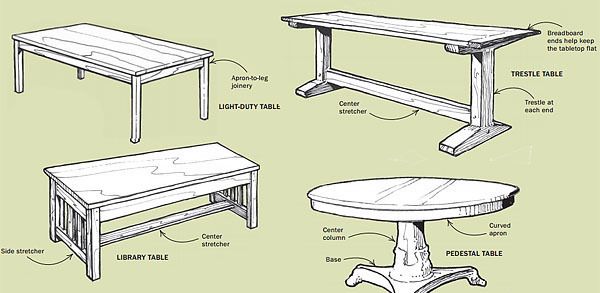
Synopsis: The best-designed tables combine basic ergonomics and proper dimensions with style. As Graham Blackburn describes, choosing a table design means paying attention to details such as comfort, size and seating capacity, functionality, and pleasing proportions.
Tables must above all function on a practical level. So far as function goes, ergonomic decisions, the choice of material, construction method, joinery details, and finish are of greatest importance. But — and this is a very big ‘but’ — for a table to be completely successful, aesthetic considerations are also extremely important.
For dining tables, the design begins with seating capacity. Unless you are planning to use extension leaves, you have to decide how many people you want the table to accommodate and live with that. Although it may be tempting to build a large table to account for any eventuality, you should consider how the table functions on a daily basis for the immediate family. If you need flexibility, extension tables are the best option but will require more effort to engineer the leaf supports.
With work tables, height might be the most important consideration. For example, a writing table will be too high for use as a computer table unless the accommodation is made for a keyboard tray. Occasional tables have their own requirements, but height and width decisions are less critical. Still, consider how they will relate to existing furniture in the home. Sofas and armchairs, for example, do not come with standard arm heights.
Regardless of your woodworking experience, the design of your particular table will benefit if you spend time identifying its precise function, giving careful consideration to the material and the construction, and following some form of aesthetic rationale throughout the piece.
TABLE HEIGHT GUIDELINESAlthough there are endless possibilities regarding style, shape, ornamentation and proportion when designing furniture, start with proven dimensions suited to the function the piece will serve. OCCASIONAL TABLES: A coffee table should afford views across a room, while an end table should be convenient to someone seated in an armchair or sofa. OCCASIONAL TABLES: A coffee table should afford views across a room, while an end table should be convenient to someone seated in an armchair or sofa. WORK TABLES: The height of a table is critical to someone who spends hours working at it. WORK TABLES: The height of a table is critical to someone who spends hours working at it. |
Function: Tables need to work as intended
The original and quintessential function of a table is to provide a flat surface for writing, playing games, eating or working. The form of any given table may be as varied as these uses. So it is of the utmost importance to be clear at the outset about the requirements of the table you intend to design. These include not only structural requirements—so that the table can do its intended job—but also ergonomic requirements. The most exquisite dining table will be a complete failure if it proves too small to sit at.
Attention to function is absolutely the designer’s first responsibility. Familiarize yourself with tables designed for similar functions, and note features designed for specific purposes, such as sturdy legs for heavy loads, drop or draw-leaves for tables that must expand, lipped tables designed to prevent objects from falling off, and added drawers or shelves for storage. A reference such as Architectural Graphic Standards (by Ramsey and Sleeper) is a useful place to explore table types by function, and a basic reference for so-called “standard” or average dimensions.
Beware of “standard” dimensions. Few people are exactly “standard.” Unless you are building many examples of a particular table, your client will be better served if the dimensions are uniquely suited to him. Nevertheless, certain aspects of many tables really shouldn’t be changed, such as the amount of leg room required beneath a skirt or the area a diner needs for greatest convenience.
THREE PATHS TO PLEASING PROPORTIONSA design rationale is crucial to building tables with pleasing proportions. The three described below are proven approaches, but others are possible. REPEATING GEOMETRIC SHAPES PROVIDE ORDER: Basic geometric shapes, such as squares, cubes, circles, ovals or ellipses, can be used to define both the overall shape and the details of a table, thereby providing it with a repeated pattern that unifies the whole structure. REPEATING GEOMETRIC SHAPES PROVIDE ORDER: Basic geometric shapes, such as squares, cubes, circles, ovals or ellipses, can be used to define both the overall shape and the details of a table, thereby providing it with a repeated pattern that unifies the whole structure. 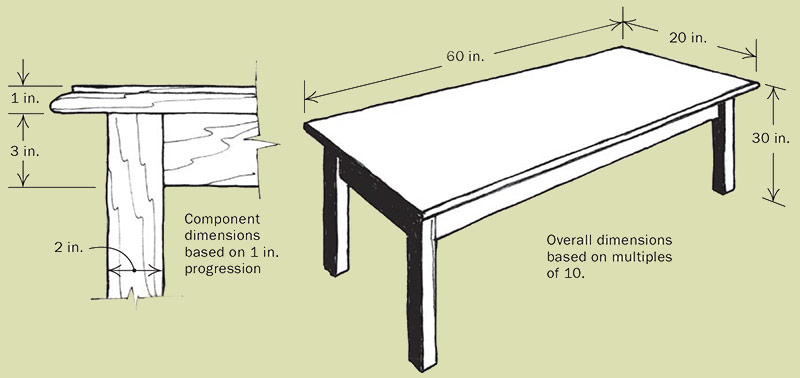 A NUMBER PROGRESSION IS A SUBTLE DESIGN DEVICE: Starting with a 1-in. thick tabletop, for example, you might construct legs that measure 2 in. square and an apron that is 3 in. deep. Relating all dimensions to a common unit, either in multiples or regular increments, provides the table with an implied pattern that may not be immediately apparent but which lends it a fundamental unity. A NUMBER PROGRESSION IS A SUBTLE DESIGN DEVICE: Starting with a 1-in. thick tabletop, for example, you might construct legs that measure 2 in. square and an apron that is 3 in. deep. Relating all dimensions to a common unit, either in multiples or regular increments, provides the table with an implied pattern that may not be immediately apparent but which lends it a fundamental unity.  CLASSICAL PROPORTION SYSTEM PLEASES THE EYE: The Golden Mean is the ratio of 1 to 1.618, represented by the Greek letter phi (φ). A table top might be designed so that its long side was 1.618 times longer than its short side. The ratio might also be used to determine the dimensions of the various parts of a table. The apron might be φ times the width of a leg, the leg φ times the thickness of the table top. CLASSICAL PROPORTION SYSTEM PLEASES THE EYE: The Golden Mean is the ratio of 1 to 1.618, represented by the Greek letter phi (φ). A table top might be designed so that its long side was 1.618 times longer than its short side. The ratio might also be used to determine the dimensions of the various parts of a table. The apron might be φ times the width of a leg, the leg φ times the thickness of the table top. |
More to a table than function and style
A table may also be defined by various structural features. The construction should, of course, be consistent with the intended use: a knock-down trestle table for portability; a draw-leaf table for occasional enlargement.
Frequently, there are trade-offs to be considered. A gate-leg table, for example, has leaves that enlarge it when needed. The leaves are supported by hinged legs that swing out. When folded, the leaves can interfere with seating, and when opened, there sometimes seems an inordinate number of legs that get in the way of diners’ legs. A group of four nesting tables stored in the space of one, great for occasional use. However, they are sequential in height and either the tallest or the shortest is apt to be at a less-than-optimal level.
While your own experience and available tools will dictate to a large extent how any given table is constructed, resist the impulse to build only what you are comfortable with. It is worth the effort to research a new technique or a new joint for the sake of better function or a more pleasing shape.
At the same time, do not get carried away by the urge for novelty. Successful construction entails the use of appropriate species, relevant construction methods, the right joint for the job — dovetail, mortise-and-tenon, dowels, biscuits, etc. — and a finish consistent with the intended use.
Legs set the style
To a great extent, all table tops are the same. They’re flat and intended to support something. While the wood species, edge treatment, and apron certainly can make stylistic statements, it is the legs that most clearly establish a table’s style and visual effect. As important as well-designed legs are, they will only be successful if they are considered as part of the overall design.
When viewing a table in a room that has enough light to make out forms but not details or wood species, it is still possible to discern the function of the table by looking at the legs. Four heavy legs joined by a horizontal stretcher tell us that this is a library table intended to support a load of books. Light and gracefully tapered legs that focus attention on the tabletop, as if it were floating, suggest that this may be a hall table for the display of some precious ornament.
Legs are frequently the key determinant of the table’s style. For example, a Queen Anne table’s top and apron are typified by restrained ornamentation. It is the cabriole legs that allow us to recognize the style. The same is true of the Shaker style, whose simple and efficient legs carry their load with no ornamentation or excess weight. And the Art Deco tables designed in the 1920s by Émile-Jacques Ruhlmann cast away traditionalism in favor of legs whose sensuous curves resembled nothing that had gone before. (See the back cover for a modern interpretation of Ruhlmann.)
TABLE BASE OPTIONSNot only must legs be appropriately sized to support the table top, they’re usually the element that makes the strongest design statement. SIMPLE LEG AND APRON CONSTRUCTION: For lighter-duty tables, this basic joinery (left) is stiff enough, and provides a light, graceful look. Stretchers can add both physical and visual sturdiness to tables that bear heavier loads (right). SIMPLE LEG AND APRON CONSTRUCTION: For lighter-duty tables, this basic joinery (left) is stiff enough, and provides a light, graceful look. Stretchers can add both physical and visual sturdiness to tables that bear heavier loads (right). 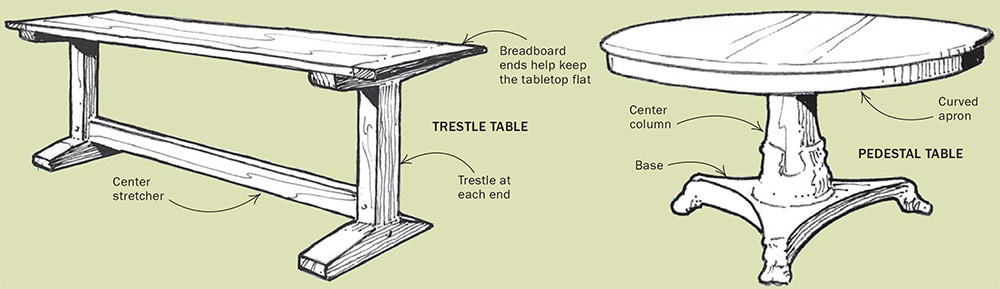 TWO OTHER TIME HONORED SYSTEMS: Dining tables must provide room for people to sit. Both the trestle and pedestal designs accomplish this by minimizing the number of table legs. The legs of trestle tables typically are set in from the end, making room all around for chairs. TWO OTHER TIME HONORED SYSTEMS: Dining tables must provide room for people to sit. Both the trestle and pedestal designs accomplish this by minimizing the number of table legs. The legs of trestle tables typically are set in from the end, making room all around for chairs. |
Develop a plan that ties together all the elements
The final ingredient for successful table design requires that every detail be considered from the point of view of how the table will look.
Given that the functional requirements have been satisfied, and that the construction is sufficiently workmanlike, the most striking feature of any table is how well it fits in with its surroundings. This can mean designing in an established style such as Queen Anne or Arts and Crafts, or designing so that the general proportions, shapes, and colors are compatible with neighboring pieces. Compatibility can result from similarity or contrast. A severely modern design might fit very well with the relatively simple lines of a room full of Shaker furniture but might look uncomfortably out of place in a room furnished in a ponderous Gothic or an ornate 18th-century style.
Designing in a particular period style can be difficult without understanding the underlying design sensibility of the period. It is not enough to employ superficial features of a period to achieve the right feeling. Slapping some mis-proportioned cabriole legs onto a table does not guarantee that it will look “Chippendale.” Incorrect details can produce ludicrous and unhappy results, similar to applying a distinctive Rolls-Royce hood to a Volkswagen Beetle.
Arts and Crafts furniture is not as uncompromisingly rectilinear as it may initially appear. And Shaker furniture, for all its apparent simplicity and lack of ornament, is often surprisingly sophisticated in its proportions. Before attempting to design a table in a period style, make sure that you understand the typical construction techniques, the common materials, and the forms that governed the proportions.
This last point— forms that govern proportions — is more important than almost anything else. The term simply means that functional and structural requirements aside, some method has been employed to decide on all the dimensional details of your table. Making decisions about the exact width of a leg or the depth of a skirt or apron based on structural requirements alone may guarantee solid joinery, but unless you are the rare designer possessed of an inherently perfect “eye” it is unlikely that your table will look as balanced and graceful as it could if designed according to some plan.
There are, in fact, numerous design paradigms commonly used by designers, some exceedingly simple, others more sophisticated. You may, indeed, invent your own paradigm or plan — the point is that using virtually any plan is better than making decisions about exact dimensions based on nothing more than what material is conveniently to hand, or what size router bits are available.
EXPANDING TABLESThe ability to expand can greatly enhance a table’s utility, but this versatility comes with challenges. Sturdiness and leaf storage are two prime considerations. HINGED LEAVES EXPAND TABLE SIDEWAYS: A pair of arms on each side hinge out to support the leaves. The disadvantage is that when folded, the leaves can intrude into the seating space below.PULL-OUT ARMS SUPPORT LEAVES: Arms that slide out from the ends of the table provide the support for end leaves. There’s no internal space for them, so the leaves must be stored elsewhere. HINGED LEAVES EXPAND TABLE SIDEWAYS: A pair of arms on each side hinge out to support the leaves. The disadvantage is that when folded, the leaves can intrude into the seating space below.PULL-OUT ARMS SUPPORT LEAVES: Arms that slide out from the ends of the table provide the support for end leaves. There’s no internal space for them, so the leaves must be stored elsewhere. DOVETAILED SLIDES SUPPORT A CENTER LEAF: Tables built this way often have multiple leaves to accommodate varying numbers of diners. Again, the unused leaves must find a home in some closet.FOLDING TOP RESTS ON GATE LEG: With the top folded, this Federal demi-lune table tucks neatly against wall. When needed, gate legs swing out from the back, and the top folds open. DOVETAILED SLIDES SUPPORT A CENTER LEAF: Tables built this way often have multiple leaves to accommodate varying numbers of diners. Again, the unused leaves must find a home in some closet.FOLDING TOP RESTS ON GATE LEG: With the top folded, this Federal demi-lune table tucks neatly against wall. When needed, gate legs swing out from the back, and the top folds open. |

 TABLE SIZE AND SEATING CAPACITY: While 29 in. elbow room per person is ideal, it’s not an unbreakable rule. Less space can be allotted at the corners, and more space is rarely a problem.
TABLE SIZE AND SEATING CAPACITY: While 29 in. elbow room per person is ideal, it’s not an unbreakable rule. Less space can be allotted at the corners, and more space is rarely a problem.